The protonmotive force and respiratory control: Difference between revisions
From Bioblast
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MITOEAGLE}} | {{MITOEAGLE}} | ||
[[File:OXPHOS-coupled energy cycles.jpg|right|300px|thumb|OXPHOS-coupled energy cycles. From [[Gnaiger_2014_MitoPathways#Chapter_1._Real-time_OXPHOS_analysis |Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways]].]] | |||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
::::» [[MITOEAGLE protocols, terminology, documentation |WG1 Project application]] | ::::» [[MITOEAGLE protocols, terminology, documentation |WG1 Project application]] | ||
[[File: | [[File:EPL-free and excess.jpg|right|300px|thumb|Capacities of the electron transfer system, oxidative phosphorylation and resting LEAK respiration (ETS, OXPHOS, LEAK) and four-compartmental OXPHOS model. (i) Capacity of the ETS module, ''E'', in the noncoupled state, generating the protonmotive force, Δ''p''<sub>mt</sub>. OXPHOS capacity, ''P'', is partitioned into (ii) the dissipative LEAK component, ''L'' (disspation of Δ''p''<sub>mt</sub>), and (iii) the free OXPHOS capacity, ''≈P=P-L'' (energy conversion driven by Δ''p''<sub>mt</sub>). If ''≈P'' is limited by the capacity of the phosphorylation system, then (iv) the apparent ETS excess capacity, ''ExP=E-P'', is available to drive coupled processes other than phosphorylation without competing with ATP production. Free divided by total ETS capacity, ''≈E/E'', is the ETS coupling efficiency. Free divided by total OXPHOS capacity, ''≈P/P'', is the OXPHOS coupling efficiency. From [[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways]].]] | ||
== Mitochondrial respiratory coupling control - a conceptual perspective on terminology == | == Mitochondrial respiratory coupling control - a conceptual perspective on terminology == | ||
::: '''Scope of MITOEAGLE publication: Respiratory states''' | ::: '''Scope of MITOEAGLE publication: Respiratory states''' | ||
::::* Target a broad audience – also the new generation | ::::* Target a broad audience – also the new generation | ||
::::* List of terms including historical terms; abbreviations (mtDNA, mt to abbreviate mitochondr*) | ::::* List of terms including historical terms; abbreviations (mtDNA, mt to abbreviate mitochondr*); OXPHOS capacity versus State 3 (discuss saturating ADP/Pi .. concentrations) | ||
::::* Scientific terminology should be general and platform independent - demands of the working groups | ::::* Scientific terminology should be general and platform independent - demands of the working groups | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
::::* [[Gnaiger_2014_MitoPathways#Chapter_2._Respiratory_states:_coupling_control |Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways]] | |||
::::* Lemieux H, Blier PU, Gnaiger E (2017) Remodeling pathway control of oxidative phosphorylation by temperature in the heart. bioRxiv doi10.1101/103457. - [[Lemieux 2017 bioRxiv |»Bioblast link«]] | ::::* Lemieux H, Blier PU, Gnaiger E (2017) Remodeling pathway control of oxidative phosphorylation by temperature in the heart. bioRxiv doi10.1101/103457. - [[Lemieux 2017 bioRxiv |»Bioblast link«]] | ||
::::* [[Miller 1991 Scientific American Library]] | ::::* [[Miller 1991 Scientific American Library]] | ||
::::* http://www.nature.com/cdd/journal/v16/n1/full/cdd2008150a.html | ::::* http://www.nature.com/cdd/journal/v16/n1/full/cdd2008150a.html | ||
::::* http://www.nature.com/cdd/journal/v20/n7/full/cdd201327a.html | ::::* http://www.nature.com/cdd/journal/v20/n7/full/cdd201327a.html | ||
== Next steps == | |||
::: Mitochondrial respiratory pathway control - substrates and inhibitors | |||
:::: Switch to pathway-related nomenclature instead of enzyme-linked terminology (N/NS/S versus CI/CI+II/CII) | |||
Revision as of 08:51, 10 April 2017
| News and Events | Working Groups | Short-Term Scientific Missions | Management Committee | Members |
COST Action CA15203 (2016-2021): MitoEAGLE
Evolution-Age-Gender-Lifestyle-Environment: mitochondrial fitness mapping
The protonmotive force and respiratory control
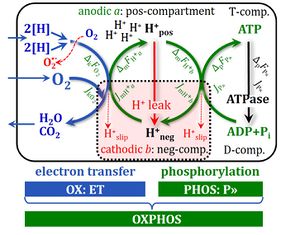
OXPHOS-coupled energy cycles. From Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways.
- » WG1 Action - WG1 MITOEAGLE protocols, terminology, documentation: Standard operating procedures and user requirement document: Protocols, terminology, documentation
- » WG1 Project application
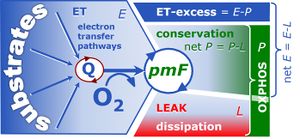
Capacities of the electron transfer system, oxidative phosphorylation and resting LEAK respiration (ETS, OXPHOS, LEAK) and four-compartmental OXPHOS model. (i) Capacity of the ETS module, E, in the noncoupled state, generating the protonmotive force, Δpmt. OXPHOS capacity, P, is partitioned into (ii) the dissipative LEAK component, L (disspation of Δpmt), and (iii) the free OXPHOS capacity, ≈P=P-L (energy conversion driven by Δpmt). If ≈P is limited by the capacity of the phosphorylation system, then (iv) the apparent ETS excess capacity, ExP=E-P, is available to drive coupled processes other than phosphorylation without competing with ATP production. Free divided by total ETS capacity, ≈E/E, is the ETS coupling efficiency. Free divided by total OXPHOS capacity, ≈P/P, is the OXPHOS coupling efficiency. From Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways.
Mitochondrial respiratory coupling control - a conceptual perspective on terminology
- Scope of MITOEAGLE publication: Respiratory states
- Target a broad audience – also the new generation
- List of terms including historical terms; abbreviations (mtDNA, mt to abbreviate mitochondr*); OXPHOS capacity versus State 3 (discuss saturating ADP/Pi .. concentrations)
- Scientific terminology should be general and platform independent - demands of the working groups
- Scope of MITOEAGLE publication: Respiratory states
- Structure
- From bioenergetics to mitochondrial physiology - historical view
- The mitochondrial respiratory system
- Rates and states - Units (important for a database); analogous to electic terms: Flow [C.s-1]; Flux [C.s-1.m-2]; Rate (?)
- Intact cells, mt preparation and normalization
- Coupling states: mt-preparations and intact cells
- Pathway states: mt-preparations and intact cells
- References
- Structure
- Journal
- Int J Biochem Cell Biol (W Koopman will be the new editor); Open Access is a requirement
- Journal
Action
References
- Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways
- Lemieux H, Blier PU, Gnaiger E (2017) Remodeling pathway control of oxidative phosphorylation by temperature in the heart. bioRxiv doi10.1101/103457. - »Bioblast link«
- Miller 1991 Scientific American Library
- http://www.nature.com/cdd/journal/v16/n1/full/cdd2008150a.html
- http://www.nature.com/cdd/journal/v20/n7/full/cdd201327a.html
Next steps
- Mitochondrial respiratory pathway control - substrates and inhibitors
- Switch to pathway-related nomenclature instead of enzyme-linked terminology (N/NS/S versus CI/CI+II/CII)
- Mitochondrial respiratory pathway control - substrates and inhibitors



