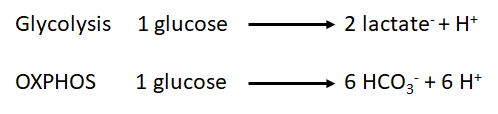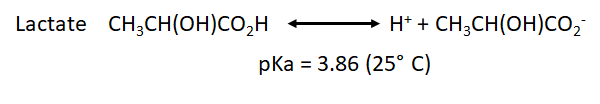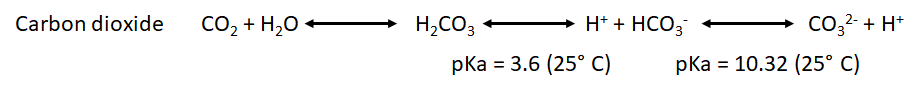Difference between revisions of "Talk:Hydrogenion flux"
m |
m |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Proton flux versus glycolytic flux == | == Proton flux versus glycolytic flux == | ||
Glycolytic flux involves 1) the conversion of glucose to pyruvate (Glycolysis) and 2) the conversion of pyruvate to lactate ( | Glycolytic flux involves 1) the conversion of glucose to pyruvate (Glycolysis) and 2) the conversion of pyruvate to lactate (cytosol) or the conversion of pyruvate into Acetyl-CoA, feeding into the TCA cycle (mitochondria). The catabolism of pyruvate can have an impact on extracellular proton flux illustrated by the following equations: | ||
Revision as of 15:34, 21 April 2020
Description
Volume-specific proton flux is measured in a closed system as the time derivative of proton concentration, expressed in units [pmol·s-1·mL-1]. It is comparable to volume-specific oxygen flux [pmol·s-1·mL-1], which is the (negative) time derivative of oxygen concentration measured in a closed system, corrected for instrumental and chemical background. Proton flux can be measured in an open system at steady state, when any acidification of the medium is compensated by external supply of an equivalent amount of base.
Abbreviation: JH+
Reference: Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways
Proton flux versus ECAR
The extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) is the change of pH in the incubation medium over time and can only be measured in a closed system. pH is the negative decadic logarithm of proton activity which is, in diluted solutions, in close approximation to the negative decadic logarithm of proton concentration. Measured changes in pH over time (ECAR) must therefore be transformed from the logarithmic to the linear scale to obtain extracellular proton flux. Therefore, ECAR is of interest in relation to acidification issues in the incubation buffer or culture medium but must not be confused with the physiologically relevant metabolic proton flux.
Proton flux versus glycolytic flux
Glycolytic flux involves 1) the conversion of glucose to pyruvate (Glycolysis) and 2) the conversion of pyruvate to lactate (cytosol) or the conversion of pyruvate into Acetyl-CoA, feeding into the TCA cycle (mitochondria). The catabolism of pyruvate can have an impact on extracellular proton flux illustrated by the following equations:
- Measurement of extracellular proton flux and glycolytic flux are related under specifically controlled conditions. Such conditions must be carefully evaluated, may require modifications of protocols, and must be corrected for acid-base reactions unrelated to glycolytic flux.
- The measurement of proton flux alone is not sufficient to determine if the origin of the protons is the glycolysis or other sources. For example, the carbon dioxide formed during the mitochondrial respiration acts as a net donor of protons into the media and as consequence has to be taken into account. During the oxidation of the glucose, we have two main metabolic pathways involved and both have a net effect over the proton flux:
-
- As we can observe, the production of protons by oxidative phosphorylation is three times higher than the one produced by the glycolysis per molecule of glucose. However, the chemical rate of production could be used to determine which is the main source of protons in our sample under specific conditions.
- We have also to take into account the pka for the point of equilibrium of the most common weak acids that will be formed during both processes:
pH changes versus glycolytic flux
- Measurement of extracellular proton flux and glycolytic flux are related under specifically conrolled conditions. Such conditions must be carefully evaluated, may require modifications of protocols, and need data analysis beyond reporting changes of pH.
- The extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) is the change of pH over time, which may be of interest in relation to acidification problems in a culture medium or incubation buffer. pH is the negative logarithm of proton activity. Comparable to volume-specific [[oxygen flux] [pmol·s-1·mL-1]], which is the (negative) time derivative of oxygen concentration measured in a closed system, volume-specific proton flux is the time derivative of proton concentration, expressed in units [pmol·s-1·mL-1]]. The physiologically relevant metabolic proton flux, therefore, must not be confused with ECAR.
- » Proton flux
- To accurately measure biologically induced changes in pH, the buffering capacity of the medium has to be small. This may be addressed either by using or preparing media with a buffering capacity that is low but still sufficient to keep the pH in the desired range for a limited period of time. An alternative approach is to use buffers with very low buffering capacity and keep the pH value inside the desired limits by a pH-Stat.
Measurement of proton flux with the O2k-pH ISE-Module
- The Oroboros O2k supports the modular O2k-MultiSensor extension for recording potentiometric (voltage) signals simultaneously with the oxygen signals in both O2k-chambers. Potentiometric measurements result in a voltage signal (pX) which is typically a linear function of the logarithm of the activity (concentration) of the substance of interest (the analyte). A calibrated pH electrode displays the negative decadic logarithm of the H+ ion activity (potentia hydrogenii) and thus got its name “pH electrode”. Using the O2k-pH ISE-Module,the extracellular proton flux can either be calculated by changes in pH over time (previous calculation of buffering capacity of the medium required) or by the amount of injected base via pH Stat. MiPNet23.15 O2k-pH ISE-Module
Additional resources
» O2k-Manual: MiPNet23.15 O2k-pH ISE-Module
» O2k-SOP: MiPNet08.16 pH calibration
» MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry: O2k hardware
MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry:
O2k-Open Support
O2k signal and output
- O2k signal: The O2k-pH ISE-Module is operated through the pX channel of the O2k, with electric potential (volt [V]) as the primary and raw signal
- O2k output: type I and II
Compare measurement of pH with the pH electrode and ratiometric fluorometric methods (NextGen-O2k)
- » Carboxy SNARF 1
- » HPTS
Applications
- For simultaneous measurement of O2 and pH, we refer to the classical literature on bioenergetics and the discovery of the chemiosmotic coupling mechanism, the quantification of H+/O2 stoichiometric ratios for proton pumping (Peter Mitchell). Other groups (e.g. SE_Lund_Elmer E) have used the pH electrode in the O2k in conjunction with a study of mitochondrial permeability transition.
- The majority of novel applications will address the problem of aerobic glycolysis in intact cells, using the measurement of proton production as an indirect but continuous record of lactate production and corresponding acidification of the medium, while simultaneously monitoring oxygen concentration and oxygen consumption. In a well buffered culture medium, the pH change is extremely small relative to the amount of protons (lactic acid) produced, hence a low-buffering capacity medium needs to be applied. A titration of acid (lactic acid or HCl) into the low-buffering capacity medium yields the pH-dependent buffering capacity (Delta H+ added/Delta H+ measured by the pH electrode). Under various metabolic conditions, lactic acid production is the dominant mechanism causing acidification, hence the pH measurement is a good indirect indicator of aerobic glycolysis.
- Bioblast links: pH and protons - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- pH and protons
- » pH
- » hydrogen ion H+
- » hydron H+
- » hydronium ion H3O+
- » hydride H-
- » proton p+
- » pH buffering capacity
- » proton flux
- » proton pump versus hydrogen ion pump
- » proton leak
- » proton slip
- » protonmotive force
- pH and protons
- O2k-pH
- » O2k-Catalogue: O2k-pH ISE-Module
- » O2k-Manual pH electrode: MiPNet23.15 O2k-pH ISE-Module
- » O2k-SOP: MiPNet08.16 pH calibration
- » File:PH-Calibration-List.xls
- » NextGen-O2k, ratiometric: Carboxy SNARF 1
- » NextGen-O2k, ratiometric: HPTS
- » pH calibration buffers
- O2k-pH
- O2k-Publications
- HRFR - general
- » O2k-Manual: MiPNet22.11 O2k-FluoRespirometer manual
- » O2k signals and output
- » O2k-SOP: MiPNet14.06 Instrumental O2 background
- » MiPNet19.18A O2k-Series G: Start
- » ESD
- » O2k configuration
- » O2k control
- » O2k-FluoRespirometer
- » O2k-Main Unit#O2k-Series
- » Titration-Injection microPump
- » Compare: O2k-TPP+_ISE-Module
- HRFR - general
- DatLab
References
- O2k-Manual: Contents: O2k-Core Manual.pdf
| Chapter | Section | Last update |
|---|---|---|
| MiPNet07.08 User information | O2k-Manual: user information. PLEASE STUDY THIS MANUAL. | 2017-11-03 |
| MiPNet19.18 O2k-Series G Core manual | O2k-Core manual contents. | 2016-08-08 |
| MiPNet19.18B POS-service | Service of the polarographic oxygen sensor OroboPOS. | 2021-06-23 |
| MiPNet19.18C DatLab 6: Guide | DatLab-guide through the menus. | 2016-08-24 |
| MiPNet19.18E O2 flux analysis - DatLab 6 | Oxygen flux analysis: DatLab real-time. | 2016-08-08 |
| MiPNet26.06 DatLab 7: Guide | DatLab-guide through the menus. | 2021-06-02 |
| MiPNet28.10 SmartPOS-service | SmartPOS: Service | 2023-09-29 |
- TIP2k-Manual***
- » O2k-Catalogue: TIP2k
- » O2k-Publications: TIP2k
| Chapter | Section | Last update |
|---|---|---|
| MiPNet12.10 TIP2k-manual | Titration-Injection microPump TIP2k manual. | 2021-07-08 |
- Bioblast links: pH and protons - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- pH and protons
- » pH
- » hydrogen ion H+
- » hydron H+
- » hydronium ion H3O+
- » hydride H-
- » proton p+
- » pH buffering capacity
- » proton flux
- » proton pump versus hydrogen ion pump
- » proton leak
- » proton slip
- » protonmotive force
- pH and protons
- O2k-pH
- » O2k-Catalogue: O2k-pH ISE-Module
- » O2k-Manual pH electrode: MiPNet23.15 O2k-pH ISE-Module
- » O2k-SOP: MiPNet08.16 pH calibration
- » File:PH-Calibration-List.xls
- » NextGen-O2k, ratiometric: Carboxy SNARF 1
- » NextGen-O2k, ratiometric: HPTS
- » pH calibration buffers
- O2k-pH
- O2k-Publications
- HRFR - general
- » O2k-Manual: MiPNet22.11 O2k-FluoRespirometer manual
- » O2k signals and output
- » O2k-SOP: MiPNet14.06 Instrumental O2 background
- » MiPNet19.18A O2k-Series G: Start
- » ESD
- » O2k configuration
- » O2k control
- » O2k-FluoRespirometer
- » O2k-Main Unit#O2k-Series
- » Titration-Injection microPump
- » Compare: O2k-TPP+_ISE-Module
- HRFR - general
- DatLab
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry,
Fluorimetry