Difference between revisions of "Glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state"
(Created page with "{{MitoPedia |abbr=G |description='''G''': Glutamate as the sole fuel substrate is transported by the electroneutral glutamate-/OH- exchanger, and is oxidised via glutamate dehydr...") |
|||
| (27 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr=G | |abbr=G | ||
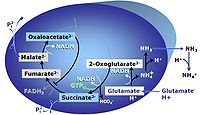
|description='''G''': Glutamate as the sole fuel substrate is transported by the electroneutral glutamate-/OH- exchanger, and is oxidised via glutamate dehydrogenase in the mitochondrial matrix. | |description=[[File:G.jpg|left|200px|G]] '''G''': [[Glutamate]] is an [[Anaplerotic pathway control state |anaplerotic]] [[Electron-transfer-pathway state |NADH-linked type 4 substrate]] (N). When supplied as the sole fuel substrate in the '''glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state''', G is transported by the electroneutral glutamate-/OH- exchanger, and is oxidised via mt-[[glutamate dehydrogenase]] in the mitochondrial matrix. The G-pathway plays an important role in [[glutaminolysis]]. | ||
|info=[[Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways]] | |||
}} | |||
Communicated by [[Gnaiger E]] 2016-01-25, edited 2016-11-29. | |||
__TOC__ | |||
== G(L) == | == G(L) == | ||
LEAK state (''L'') with G alone as substrate can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocol: | |||
:::*[[SUIT-007]] | |||
::::* DL-Protocol for permeabilized cells (pce): [[SUIT-007 O2 ce-pce D030]] | |||
== G(P) == | == G(P) == | ||
OXPHOS state (''P'') with G alone as substrate can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocol: | |||
:::*[[SUIT-007]] | |||
::::* DL-Protocol for permeabilized cells (pce): [[SUIT-007 O2 ce-pce D030]] | |||
== G(E) == | == G(E) == | ||
ET state (''E'') with G alone as substrate can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocol: | |||
:::*[[SUIT-007]] | |||
::::* DL-Protocol for permeabilized cells (pce): [[SUIT-007 O2 ce-pce D030]] | |||
== Details == | == Details == | ||
In human skeletal muscle mitochondria, [[OXPHOS]] capacity with glutamate alone is 50% to 85% of respiration | :::: In '''human skeletal muscle mitochondria''', [[OXPHOS]] capacity with glutamate alone (G<sub>''P''</sub>) is 50% to 85% of respiration in the [[GM-pathway control state]] (GM<sub>''P''</sub>). Accumulation of fumarate inhibits succinate dehydrogenase and glutamate dehydrogenase. | ||
Glutamate derived from hydrolyzation of glutamine is an important aerobic substrate in cultured cells. Mitochondrial glutamate dehydrogenase is particularly active in astrocytes, preventing glutamate induced neurotoxicity. mtNAD-malic enzyme supports an anaplerotic pathway when carbohydrate is limiting. | |||
:::: Glutaminolysis: Glutamate derived from hydrolyzation of glutamine is an important aerobic substrate in cultured cells, supporting anaplerosis. Mitochondrial glutamate dehydrogenase is particularly active in astrocytes, preventing glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. | |||
:::: Anaplerosis from malate: mtNAD-malic enzyme supports an anaplerotic pathway when carbohydrate is limiting. | |||
== [[SUITbrowser]] question: Glutamine/glutamate == | |||
:::: The [https://suitbrowser.oroboros.at/ SUITbrowser] can be used to find the best SUIT protocols to analyse glutamine/glutamate metabolism, among other research questions. | |||
{{MitoPedia concepts | |||
|mitopedia concept=SUIT state | |||
}} | |||
Latest revision as of 20:11, 1 January 2021
- high-resolution terminology - matching measurements at high-resolution
Glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state
Description
G: Glutamate is an anaplerotic NADH-linked type 4 substrate (N). When supplied as the sole fuel substrate in the glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state, G is transported by the electroneutral glutamate-/OH- exchanger, and is oxidised via mt-glutamate dehydrogenase in the mitochondrial matrix. The G-pathway plays an important role in glutaminolysis.
Abbreviation: G
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
Communicated by Gnaiger E 2016-01-25, edited 2016-11-29.
G(L)
LEAK state (L) with G alone as substrate can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocol:
-
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized cells (pce): SUIT-007 O2 ce-pce D030
-
G(P)
OXPHOS state (P) with G alone as substrate can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocol:
-
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized cells (pce): SUIT-007 O2 ce-pce D030
-
G(E)
ET state (E) with G alone as substrate can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocol:
-
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized cells (pce): SUIT-007 O2 ce-pce D030
-
Details
- In human skeletal muscle mitochondria, OXPHOS capacity with glutamate alone (GP) is 50% to 85% of respiration in the GM-pathway control state (GMP). Accumulation of fumarate inhibits succinate dehydrogenase and glutamate dehydrogenase.
- Glutaminolysis: Glutamate derived from hydrolyzation of glutamine is an important aerobic substrate in cultured cells, supporting anaplerosis. Mitochondrial glutamate dehydrogenase is particularly active in astrocytes, preventing glutamate-induced neurotoxicity.
- Anaplerosis from malate: mtNAD-malic enzyme supports an anaplerotic pathway when carbohydrate is limiting.
SUITbrowser question: Glutamine/glutamate
- The SUITbrowser can be used to find the best SUIT protocols to analyse glutamine/glutamate metabolism, among other research questions.
MitoPedia concepts:
SUIT state