Difference between revisions of "Flow"
(Created page with "{{MitoPedia |abbr=''I'' |description=In an isomorphic analysis, any form of '''flow''', ''I'' is the advancement of a process per unit of time, expressed in a specific mot...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr=''I'' | |abbr=''I'' | ||
|description=In an isomorphic analysis, any form of '''flow''', ''I'' is the [[advancement]] of a process per unit of time, expressed in a specific motive unit [MU∙s<sup>-1</sup>], ''e.g.'', ampere for electric flow or current [A≡C∙s<sup>-1</sup>], watt for heat flow [W≡J∙s<sup>-1</sup>], and for chemical flow the unit is [mol∙s<sup>-1</sup>]. The corresponding isomorphic [[force]]s are the partial exergy (Gibbs energy) changes per advancement [J∙MU<sup>-1</sup>], expressed in volt for electric force [V≡J∙C<sup>-1</sup>], dimensionless for thermal force, and for chemical force the unit is [J∙mol<sup>-1</sup>], which deserves a specific acronym ([Jol]) comparable to volt. | |description=In an isomorphic analysis, any form of '''flow''', ''I'' is the [[advancement]] of a process per unit of time, expressed in a specific motive unit [MU∙s<sup>-1</sup>], ''e.g.'', ampere for electric flow or current [A≡C∙s<sup>-1</sup>], watt for heat flow [W≡J∙s<sup>-1</sup>], and for chemical flow the unit is [mol∙s<sup>-1</sup>]. Flow is an [[extensive quantity]]. The corresponding isomorphic [[force]]s are the partial exergy (Gibbs energy) changes per advancement [J∙MU<sup>-1</sup>], expressed in volt for electric force [V≡J∙C<sup>-1</sup>], dimensionless for thermal force, and for chemical force the unit is [J∙mol<sup>-1</sup>], which deserves a specific acronym ([Jol]) comparable to volt. | ||
|info=[[ | |info=[[Gnaiger_1993_Pure Appl Chem]], [[MitoEAGLE preprint 2018-02-08]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia concepts | {{MitoPedia concepts | ||
|mitopedia concept=MiP concept | |mitopedia concept=MiP concept, Ergodynamics | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia methods}} | {{MitoPedia methods}} | ||
{{MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry}} | {{MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry}} | ||
{{MitoPedia topics}} | {{MitoPedia topics}} | ||
<gallery heights="350px" mode="default" perrow="4" widths="350px"> | |||
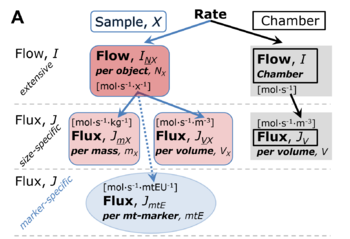
File:Rate.png |'''Normalization of rate.''' '''(A)''' Cell respiration is normalized for (1) the experimental '''Sample''' (flow per object, mass-specific flux, or cell-volume-specific flux); or (2) for the '''Chamber''' volume. Normalization yields the [[specific quantity]] ''[[flux]]'' from the [[extensive quantity]] ''flow''. From [[MitoEAGLE preprint 2018-02-08]]. | |||
</gallery> | |||
Revision as of 21:43, 23 August 2018
Description
In an isomorphic analysis, any form of flow, I is the advancement of a process per unit of time, expressed in a specific motive unit [MU∙s-1], e.g., ampere for electric flow or current [A≡C∙s-1], watt for heat flow [W≡J∙s-1], and for chemical flow the unit is [mol∙s-1]. Flow is an extensive quantity. The corresponding isomorphic forces are the partial exergy (Gibbs energy) changes per advancement [J∙MU-1], expressed in volt for electric force [V≡J∙C-1], dimensionless for thermal force, and for chemical force the unit is [J∙mol-1], which deserves a specific acronym ([Jol]) comparable to volt.
Abbreviation: I
Reference: Gnaiger_1993_Pure Appl Chem, MitoEAGLE preprint 2018-02-08
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
Ergodynamics
Normalization of rate. (A) Cell respiration is normalized for (1) the experimental Sample (flow per object, mass-specific flux, or cell-volume-specific flux); or (2) for the Chamber volume. Normalization yields the specific quantity flux from the extensive quantity flow. From MitoEAGLE preprint 2018-02-08.