Difference between revisions of "Extensive quantity"
| (10 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|description='''Extensive quantities''' pertain to a total system, e.g. [[oxygen flow]]. | |description='''Extensive quantities''' pertain to a total system, e.g. [[oxygen flow]]. An extensive quantity increases proportional with system size. The magnitude of an extensive quantity is completely additive for non-interacting subsystems, such as mass or flow expressed per defined system. The magnitude of these quantities depends on the extent or size of the system ([[Cohen 2008 IUPAC Green Book |Cohen et al 2008]]). | ||
|info=[[ | |info=[[BEC 2020.1]], [[Gnaiger_1993_Pure Appl Chem]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
<gallery heights="350px" mode="default" perrow="4" widths="350px"> | |||
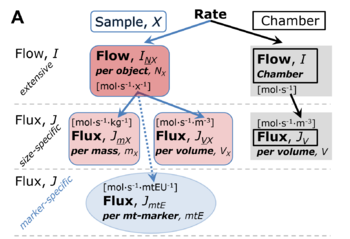
File:Rate.png |'''Normalization of rate.''' '''(A)''' Cell respiration is normalized for (1) the experimental '''Sample''' (flow per object, mass-specific flux, or cell-volume-specific flux); or (2) for the '''Chamber''' volume. Flow per object and flow per system are extensive quantities. From [[Gnaiger 2019 MitoFit Preprints]]. | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Compare == | |||
::::* [[Extensive quantity]] | |||
::::* [[Specific quantity]] | |||
::::* [[Intensive quantity]] | |||
{{Template:Keywords: Normalization}} | |||
{{MitoPedia concepts | {{MitoPedia concepts | ||
|mitopedia concept=MiP concept | |mitopedia concept=MiP concept, Ergodynamics | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{Labeling | {{Labeling | ||
|instruments=Theory | |instruments=Theory | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 12:17, 16 October 2022
Description
Extensive quantities pertain to a total system, e.g. oxygen flow. An extensive quantity increases proportional with system size. The magnitude of an extensive quantity is completely additive for non-interacting subsystems, such as mass or flow expressed per defined system. The magnitude of these quantities depends on the extent or size of the system (Cohen et al 2008).
Reference: BEC 2020.1, Gnaiger_1993_Pure Appl Chem
Normalization of rate. (A) Cell respiration is normalized for (1) the experimental Sample (flow per object, mass-specific flux, or cell-volume-specific flux); or (2) for the Chamber volume. Flow per object and flow per system are extensive quantities. From Gnaiger 2019 MitoFit Preprints.
Compare
- Bioblast links: Normalization - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Quantities for normalization
- » Count in contrast to Number
- » Mitochondrial marker
- » O2k-Protocols: mitochondrial and marker-enzymes
- » Citrate synthase activity
- Quantities for normalization
- General
- Related keyword lists
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
Ergodynamics
Labels:
HRR: Theory