PGMS-pathway control state: Difference between revisions
From Bioblast
Beno Marija (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia concepts | {{MitoPedia concepts | ||
|mitopedia concept= | |mitopedia concept=SUIT state | ||
}} | }} | ||
== PGMS(L) == | == PGMS(L) == | ||
Revision as of 12:20, 19 November 2016
Description
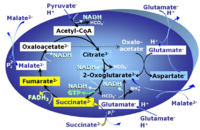
PGMS: Pyruvate & Glutamate & Malate & Succinate.
MitoPathway control state: NS
2-oxoglutarate is produced through the citric acid cycle from citrate by isocitrate dehydrogenase, from oxaloacetate and glutamate by the transaminase, and from glutamate by the glutamate dehydrogenase. If the 2-oxoglutarate carrier does not outcompete these sources of 2-oxoglutarate, then the TCA cycle operates in full circle with external pyruvate&malate&glutamate&succinate
Abbreviation: PGMS
Reference: Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways - Chapter 5.6
MitoPedia concepts:
SUIT state
PGMS(L)
PGMS(P)
PGMS(E)
Discussion
- Recent studies showed that S- and NS-linked OXPHOS capacity is inhibited by 2 mM malate concentrations as applied in many SUIT protocols. This inhibition is less pronounced at higher succinate concentrations (10 mM up to 50 mM S).