Difference between revisions of "Zapico 2013 Aging Dis"
(Created page with "{{Publication |title=Zapico SC, Ubelaker DH (2013) mtDNA mutations and their role in aging, diseases and forensic sciences. Aging Dis 4:364-80. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.201...") |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|editor=Gnaiger E | |editor=Gnaiger E | ||
}} | }} | ||
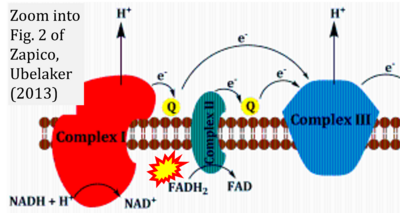
[[File:Zapico 2013 Aging Dis CORRECTION.png|right|400px]] | [[File:Zapico 2013 Aging Dis CORRECTION.png|right|400px]] | ||
{{Template:Correction FADH2 and S-pathway}} | {{Template:Correction FADH2 and S-pathway}} | ||
{{Labeling | {{Labeling | ||
|pathways=S | |pathways=S | ||
}} | }} | ||
Latest revision as of 21:45, 18 December 2023
| Zapico SC, Ubelaker DH (2013) mtDNA mutations and their role in aging, diseases and forensic sciences. Aging Dis 4:364-80. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2013.0400364 |
Zapico SC, Ubelaker DH (2013) Aging Dis
Abstract: Mitochondria are independent organelles with their own DNA. As a primary function, mitochondria produce the energy for the cell through Oxidative Phosphorylation (OXPHOS) in the Electron Transport Chain (ETC). One of the toxic products of this process is Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS), which can induce oxidative damage in macromolecules like lipids, proteins and DNA. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is less protected and has fewer reparation mechanisms than nuclear DNA (nDNA), and as such is more exposed to oxidative, mutation-inducing damage. This review analyzes the causes and consequences of mtDNA mutations and their relationship with the aging process. Neurodegenerative diseases, related with the aging, are consequences of mtDNA mutations resulting in a decrease in mitochondrial function. Also described are "mitochondrial diseases", pathologies produced by mtDNA mutations and whose symptoms are related with mitochondrial dysfunction. Finally, mtDNA haplogroups are defined in this review; these groups are important for determination of geographical origin of an individual. Additionally, different haplogroups exhibit variably longevity and risk of certain diseases. mtDNA mutations in aging and haplogroups are of special interest to forensic science research. Therefore this review will help to clarify the key role of mtDNA mutations in these processes and support further research in this area.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Labels:
Pathway: S