Difference between revisions of "Template:SUIT-002"
From Bioblast
Leo Elettra (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:SUIT-MitoFit.png|right|190px|link=http://www.bioblast.at/index.php/MitoPedia:_SUIT |MitoPedia: SUIT]] | [[Image:SUIT-MitoFit.png|right|190px|link=http://www.bioblast.at/index.php/MitoPedia:_SUIT |MitoPedia: SUIT]] | ||
== Steps and respiratory states == | == Steps and respiratory states == | ||
[[File:1D;2M.1; | [[File:1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot-.png|400px]] | ||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" | {| class="wikitable" border="1" | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1D | | 1D | ||
| [[ | | [[REN]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 3Oct | ||
| [[ | | [[OctM]]<sub>''P''</sub> | ||
| [[F]] | | [[F]] | ||
| FAO | | FAO | ||
| 1D;2M.1; | | 1D;2M.1;3Oct | ||
*{{Template:SUIT F}} | *{{Template:SUIT F}} | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 3c | | 3c | ||
| [[ | | [[OctM]]c<sub>''P''</sub> | ||
| [[F]] | | [[F]] | ||
| FAO | | FAO | ||
| 1D;2M.1; | | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;3c | ||
*{{Template:SUIT F}} | *{{Template:SUIT F}} | ||
| Line 45: | Line 45: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 4M2 | | 4M2 | ||
| [[ | | [[OctM]]<sub>''P''</sub> | ||
| [[Fatty acid oxidation pathway control state|F(N)]] | | [[Fatty acid oxidation pathway control state|F(N)]] | ||
| FAO | | FAO | ||
| 1D;2M.1; | | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;3c;4M2 | ||
*{{Template:SUIT F(N)}} | *{{Template:SUIT F(N)}} | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 5P | | 5P | ||
| [[ | | [[OctPM]]<sub>''P''</sub> | ||
| [[FN]] | |||
| FAO<small>&</small>CI | |||
| 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P | |||
*{{Template:SUIT FN}} | |||
*{{Template:SUIT OXPHOS}} | |||
|- | |||
| 6G | |||
| [[OctPGM]]<sub>''P''</sub> | |||
| [[FN]] | | [[FN]] | ||
| FAO<small>&</small>CI | | FAO<small>&</small>CI | ||
| 1D;2M.1; | | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G | ||
*{{Template:SUIT FN}} | *{{Template:SUIT FN}} | ||
| Line 65: | Line 75: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 7S | ||
| [[ | | [[OctPGMS]]<sub>''P''</sub> | ||
| [[FNS]] | | [[FNS]] | ||
| FAO<small>&</small>CI<small>&</small>II | | FAO<small>&</small>CI<small>&</small>II | ||
| 1D;2M.1; | | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S | ||
*{{Template:SUIT FNS}} | *{{Template:SUIT FNS}} | ||
| Line 75: | Line 85: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 8Gp | ||
| [[ | | [[OctPGMSGp]]<sub>''P''</sub> | ||
| [[FNSGp]] | |||
| FAO<small>&</small>CI<small>&</small>II<small>&</small>GpDH | |||
| 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp | |||
*{{Template:SUIT FNSGp}} | |||
*{{Template:SUIT OXPHOS}} | |||
|- | |||
| 9U | |||
| [[OctPGMSGp]]<sub>''E''</sub> | |||
| [[FNSGp]] | |||
| FAO<small>&</small>CI<small>&</small>II<small>&</small>GpDH | |||
| 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U | |||
*{{Template:SUIT FNSGp}} | |||
*{{Template:SUIT U*}} | |||
|- | |||
| 10Rot | |||
| [[SGp]]<sub>''E''</sub> | |||
| [[SGp]] | | [[SGp]] | ||
| CII | | CII<small>&</small>GpDH | ||
| 1D;2M.1; | | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot | ||
*{{Template:SUIT SGp}} | *{{Template:SUIT SGp}} | ||
| Line 85: | Line 115: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 11Ama | ||
| [[ROX]] | | [[ROX]] | ||
| | | | ||
| | | | ||
| 1D;2M.1; | | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot;11Ama | ||
*{{Template:SUIT Ama}} | *{{Template:SUIT Ama}} | ||
Latest revision as of 13:16, 24 January 2024
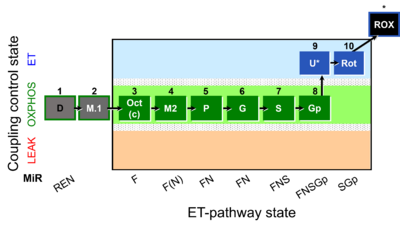
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1D | REN | 1D
| ||
| 2M.1 | 1D;2M.1 | |||
| 3Oct | OctMP | F | FAO | 1D;2M.1;3Oct
|
| 3c | OctMcP | F | FAO | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;3c
|
| 4M2 | OctMP | F(N) | FAO | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;3c;4M2
|
| 5P | OctPMP | FN | FAO&CI | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P
|
| 6G | OctPGMP | FN | FAO&CI | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G
|
| 7S | OctPGMSP | FNS | FAO&CI&II | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S
|
| 8Gp | OctPGMSGpP | FNSGp | FAO&CI&II&GpDH | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp
|
| 9U | OctPGMSGpE | FNSGp | FAO&CI&II&GpDH | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U
|
| 10Rot | SGpE | SGp | CII&GpDH | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot
|
| 11Ama | ROX | 1D;2M.1;3Oct;4M2;5P;6G;7S;8Gp;9U;10Rot;11Ama
|
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary