Difference between revisions of "R-L net ROUTINE capacity"
m (Gnaiger Erich moved page Free ROUTINE activity to Free ROUTINE-activity) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr='' | |abbr=''R-L'' | ||
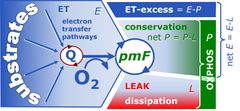
|description=[[Image:R-L.jpg|50 px|Free ROUTINE activity]] The '''free ROUTINE activity''' | |description=[[Image:R-L.jpg|50 px|Free ROUTINE-activity]] The '''free ROUTINE-activity''' is [[ROUTINE respiration]] corrected for [[LEAK respiration]], ''R-L''. ''R-L'' is the respiratory activity available for phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Oxygen consumption in the ROUTINE state of respiration measured in living cells, therefore, is partitioned into the free ROUTINE-activity, ''R-L'', strictly coupled to phosphorylation, ''P»'', and nonphosphorylating LEAK respiration, ''L<sub>R</sub>'', compensating for proton leaks, slip and cation cycling: ''R'' = ''R-L''+''L<sub>R</sub>''. It is frequently assumed that [[LEAK respiration]], ''L'', as measured in the LEAK state, overestimates the LEAK component of respiration, ''L<sub>R</sub>'', as measured in the ROUTINE-state, particularly if the protonmotive force is not adjusted to equivalent levels in ''L'' and ''L<sub>R</sub>''. However, if the LEAK component increases with enzyme turnover during ''R'', the low enzyme turnover during ''L'' may counteract the effect of the higher ''pmF''. | ||
|info=[[Gnaiger | |info=[[Gnaiger 2020 MitoPathways]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Communicated by [[Gnaiger E]] (2014-09-21) last update 2020-11-08. | |||
[[File:EPL-free and excess.jpg|right|240px|thumb|[[Gnaiger 2020 MitoPathways |The Blue Book 2014]]]] | |||
== Compare == | |||
* [[Free OXPHOS-capacity]] (mt-preparations) | |||
* [[Free ET-capacity]] | |||
{{MitoPedia concepts | {{MitoPedia concepts | ||
|mitopedia concept=Respiratory state, Recommended | |mitopedia concept=Respiratory state, Recommended | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia topics | {{MitoPedia topics | ||
|mitopedia topic=EAGLE | |mitopedia topic=EAGLE | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 10:52, 8 November 2020
Description
![]() The free ROUTINE-activity is ROUTINE respiration corrected for LEAK respiration, R-L. R-L is the respiratory activity available for phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Oxygen consumption in the ROUTINE state of respiration measured in living cells, therefore, is partitioned into the free ROUTINE-activity, R-L, strictly coupled to phosphorylation, P», and nonphosphorylating LEAK respiration, LR, compensating for proton leaks, slip and cation cycling: R = R-L+LR. It is frequently assumed that LEAK respiration, L, as measured in the LEAK state, overestimates the LEAK component of respiration, LR, as measured in the ROUTINE-state, particularly if the protonmotive force is not adjusted to equivalent levels in L and LR. However, if the LEAK component increases with enzyme turnover during R, the low enzyme turnover during L may counteract the effect of the higher pmF.
The free ROUTINE-activity is ROUTINE respiration corrected for LEAK respiration, R-L. R-L is the respiratory activity available for phosphorylation of ADP to ATP. Oxygen consumption in the ROUTINE state of respiration measured in living cells, therefore, is partitioned into the free ROUTINE-activity, R-L, strictly coupled to phosphorylation, P», and nonphosphorylating LEAK respiration, LR, compensating for proton leaks, slip and cation cycling: R = R-L+LR. It is frequently assumed that LEAK respiration, L, as measured in the LEAK state, overestimates the LEAK component of respiration, LR, as measured in the ROUTINE-state, particularly if the protonmotive force is not adjusted to equivalent levels in L and LR. However, if the LEAK component increases with enzyme turnover during R, the low enzyme turnover during L may counteract the effect of the higher pmF.
Abbreviation: R-L
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 MitoPathways
Communicated by Gnaiger E (2014-09-21) last update 2020-11-08.
Compare
- Free OXPHOS-capacity (mt-preparations)
- Free ET-capacity
MitoPedia concepts:
Respiratory state,
Recommended
MitoPedia topics:
EAGLE