Difference between revisions of "PM-pathway control state"
From Bioblast
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
'''MitoPathway control:''' CI | '''MitoPathway control:''' CI | ||
'''SUIT protocol:''' [[SUIT | '''SUIT protocol:''' [[SUIT RP1]] | ||
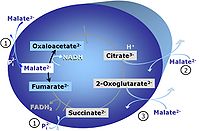
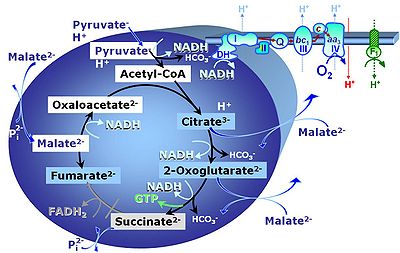
[[Pyruvate]] (P) is oxidatively decarboxylated to acetyl-CoA and CO<sub>2</sub>, yielding [[NADH]] catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase. [[Malate]] (M) is oxidized to oxaloacetate by mt-malate dehydrogenase located in the mitochondrial matrix. Condensation of oxaloacate with acetyl-CoA yields citrate (citrate synthase). 2-oxoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) is formed from isocitrate (isocitrate dehydrogenase). | [[Pyruvate]] (P) is oxidatively decarboxylated to acetyl-CoA and CO<sub>2</sub>, yielding [[NADH]] catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase. [[Malate]] (M) is oxidized to oxaloacetate by mt-malate dehydrogenase located in the mitochondrial matrix. Condensation of oxaloacate with acetyl-CoA yields citrate (citrate synthase). 2-oxoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) is formed from isocitrate (isocitrate dehydrogenase). | ||
Revision as of 12:57, 20 July 2016
Description
MitoPathway control: CI
SUIT protocol: SUIT RP1
Pyruvate (P) is oxidatively decarboxylated to acetyl-CoA and CO2, yielding NADH catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase. Malate (M) is oxidized to oxaloacetate by mt-malate dehydrogenase located in the mitochondrial matrix. Condensation of oxaloacate with acetyl-CoA yields citrate (citrate synthase). 2-oxoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) is formed from isocitrate (isocitrate dehydrogenase).
Abbreviation: PM
Reference: Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways - Chapter 3.2
MitoPedia concepts:
Respiratory state,
SUIT state
PM(L)
- SUIT RP1: 1PM 2D 2c (2NADH) 3U 4Oct 5G 6S 7Rot 8Gp 9Ama 10Tm
PM(P)
- SUIT RP1: 1PM 2D 2c (2NADH) 3U 4Oct 5G 6S 7Rot 8Gp 9Ama 10Tm
PM(E)
- SUIT RP1: 1PM 2D 2c (2NADH) 3U 4Oct 5G 6S 7Rot 8Gp 9Ama 10Tm
CI-linked linear coupling control: L – P - E
- L - P
- OXPHOS coupling efficiency (P-L or ≈P control factor), j≈P = ≈P/P = (P-L)/P = 1-L/P, is measured in the CI-linked substrate state, with defined coupling sites (CI, CIII, CIV) and at high flux.
- P - E
- CCCP is titrated stepwise to maximum flux, to evaluate limitation of OXPHOS by the phosphorylation system, expressed as the apparent excess E-P capacity factor (E-P coupling control factor), jExP = (E-P)/E = 1-P/E. If jExP>0, then the ETS coupling efficiency rather than the OXPHOS coupling efficiency is the proper expression of coupling, j≈E = ≈E/E = (E-L)/E = 1-L/E.
Discussion
- Pyruvate alone is not an ETS competent substrate state in most mt-preparations, since acetyl-CoA accumulates without the co-substrate (oxaloacetate) of citrate synthase.
- Malate alone is not an ETS competent substrate state in many mt-preparations, since oxaloacetate accumulates without the co-substrate (acetyl-CoA) of citrate synthase.