Description
The chemical potential of a substance B, µB [J/mol], is the partial derivative of Gibbs energy, G [J], per amount of B, nB [mol], at constant temperature, pressure, and composition other than that of B,
µB = (∂G/∂nB)T,p,nj≠B
The chemical potential of a solute in solution is the sum of the standard chemical potential under defined standard conditions and a concentration (activity)-dependent term,
µB = µB° + RT ln(aB)
The standard state for the solute is refered to ideal behaviour at standard concentration, c° = 1 mol/L, exhibiting infinitely diluted solution behaviour. µB° equals the standard molar Gibbs energy of formation, ΔfGB° [kJ·mol-1]. The formation process of B is the transformation of the pure constituent elements to one mole of substance B, with all substances in their standard state (the most stable form of the element at 100 kPa (1 bar) at the specified temperature).
Abbreviation: µ
Reference: Cohen 2008 IUPAC Green Book
Communicated by Gnaiger E 2018-10-18
MitoPedia concepts: Ergodynamics
The proton chemical potential
- The standard chemical potential of protons at pH = 0 is by defintion zero. Therefore, µH+ depends on the activity of protons only,
µH+ = RT ln(aH+)
Since pH = -lg(aH+), µH+ is related to pH as,
µH+ = -RT·ln(10)·pH
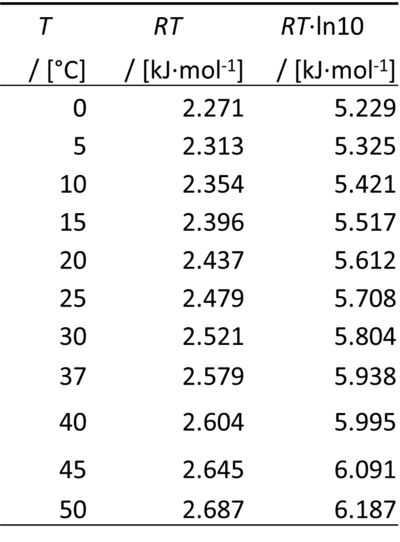
Therefore, for a difference of pH of -1 unit, ΔµH+ equals RT·ln(10):
0 °C = 273.15 K
ln(10) = 2.302585093
- At pH 7, the chemical potential of the proton at 25 °C (37 °C) is -39.956 (-41.564) kJ·mol-1.