Sleiman 2015 Abstract MiP2015
| Mitochondrial respiration in sequential biospies from skeletal muscles during hemorrhagic shock and over the course of 48h of reperfusion in pigs. |
Link:
Sleiman Y, Weidgang C, Nussbaum P, Radermacher P, Calzia E (2015)
Event: MiP2015
Previous data [1] have shown that mitochondrial respiration is severely affected during hemorrhagic shock, but rapidly recovers during reperfusion. Therefore, in our actual experiment we performed sequential measurements of mitochondrial respiratory activity during hemorrhagic shock and for up to 48 hours during reperfusion in skeletal muscles of the pig.
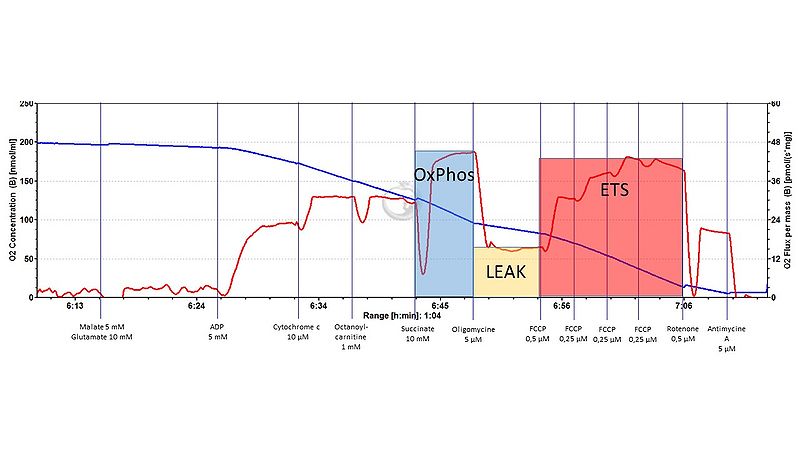
After approval by the animal ethical committee of our institution we induced hemorrhagic shock in 6 anesthetized, mechanically ventilated pigs (removal of 30% of the blood volume and subsequent blood removal/retransfusion to maintain mean arterial pressure at 40 mm Hg) for 3 hours. Then the shed blood was retransfused and the animal remained under anesthesia and mechanical ventilation for an observation period lasting for 48 hours. Skeletal muscle biopsies were taken before shock, during shock, and after 6, 12, 24, and 48 hours of recovery. The tissue samples were homogenized and put into the chambers of the O2K®-Oxygraph (Oroboros Instruments, Austria) and continuously stirred at 37°C. Mitochondrial respiration was quantified by adding complex I (10 mM Pyruvate, 5 mM Malate, and 10 mM Glutamate) and complex II (10 mM Succinate) substrates and 5 mM ADP. Then 5 µM oligomycine was added to inhibit the ATP-synthase in order to obtain the LEAK-respiration state as an indicator of mitochondrial coupling. This step was followed by the addition of 1 µM of the uncoupler FCCP in order to achive the maximum respiration in the uncoupled state and the coupling (LEAK/ET-pathway)-ratio.
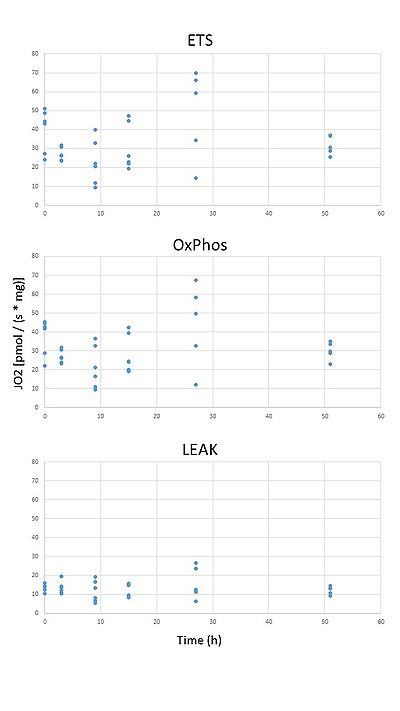
A typical oxygraph tracing as well as the preliminary results are presented in the figures below.
The overall response to hemorrhagic shock and reperfusion seems rather moderate; however, refining the targets of hemorrhagic shock, and, consequently, peripheral perfusion might still reveal a more clear picture of the effects of shock on mitochondrial respiration.
• O2k-Network Lab: DE Ulm Radermacher P
Labels: MiParea: Respiration
Stress:Ischemia-reperfusion Organism: Pig Tissue;cell: Skeletal muscle Preparation: Homogenate
Coupling state: LEAK, OXPHOS, ET
Pathway: N, S
HRR: Oxygraph-2k
Event: A1, Poster
MiP2015
Affiliations
Ulm Univ Hospital, Dept Anesthesiological Pathophysiology and Process Development, Germany. - [email protected]
Figures
References and acknowledgements
- Bracht H, Scheuerle A, Gröger M, Hauser B, Matallo J, McCook O, Seifritz A, Wachter U, Vogt JA, Asfar P, Matejovic M, Möller P, Calzia E, Szabó C, Stahl W, Hoppe K, Stahl B, Lampl L, Georgieff M, Wagner F, Radermacher P, Simon F (2012) Effects of intravenous sulfide during resuscitated porcine hemorrhagic shock. Crit Care Med 40:2157-67.