Doerrier 2019 MitoFit Preprint Arch EA
| Doerrier C, Gama-Perez P, Distefano G, Pesta D, Soendergaard SD, Chroeis KM, Gonzalez-Franquesa A, Goodpaster BH, Coen P, Larsen S, Gnaiger E, Garcia-Roves PM (2019) Inter-laboratory harmonization of respiratory protocols in permeabilized human muscle fibers. https://doi.org/10.26124/mitofit:ea19.MiPSchool.0009 |
» MitoFit Preprint Arch EA19.9
Inter-laboratory harmonization of respiratory protocols in permeabilized human muscle fibers
Doerrier C, Gama-Perez P, Distefano G, Pesta D, Soendergaard SD, Chroeis KM, Gonzalez-Franquesa A, Goodpaster BH, Coen P, Larsen S, Gnaiger Erich, Garcia-Roves PM (2019) MitoFit Preprint Arch
Abstract: Version 1 (v1) 2019-07-04 doi:10.26124/mitofit:ea19.MiPSchool.0009
Permeabilized muscle fibers are extensively used for analysis of mitochondrial function in exercise and pathophysiological studies. Inter- and intra-laboratory comparisons of published results on permeabilized muscle fibers are difficult due to application of different experimental procedures, including sample preparation, substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titrations (SUIT), respiratory media, and oxygen regimes. Oxygen dependence of mitochondrial respiration in permeabilized fibers (about 100-fold higher p50 compared to small living cells and isolated mitochondria [1]) reveals the requirement of using hyperoxic incubation conditions to avoid oxygen limitation of respiratory capacity [2]. However, controversial results on the oxygen dependence of permeabilized muscle fibers have been reported by different research groups using different respiration media in the presence or absence of the myosin II-specific inhibitor blebbistatin [3,4].
In the framework of COST Action MitoEAGLE, our main goals for the current study of permeabilized human muscle fibers are: (1) a comparison of protocols used in different research laboratories, (2) harmonization of results to address the reproducibility crisis [5], (3) evaluation of optimum experimental conditions, and (4) analysis of the causes of experimental variability.
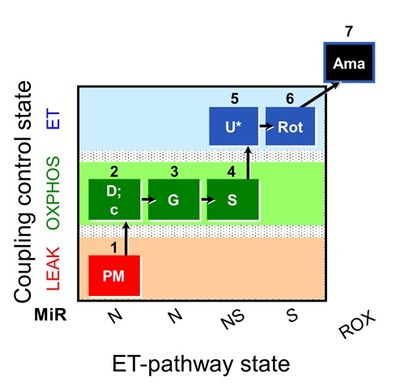
We performed a blinded test with human permeabilized skeletal fibers. Six groups from Austria, Denmark, Germany, Spain, and USA measured simultaneously in the same laboratory mitochondrial respiration using high-resolution respirometry (O2k; Oroboros Instruments, Austria) in three human biopsies (vastus lateralis) from the same healthy volunteer sampled on three consecutive days. A total of 96 (32/day) permeabilized fiber preparations were assayed. The wet mass of permeabilized fibers ranged from 0.38 to 2.83 mg per chamber. Protocols were compared at several levels: (1) permeabilized fiber preparation; (2) respiration media MiR05-Kit and Buffer Z in the presence/absence of blebbistatin (25 µM), covering the most frequently used experimental conditions in the literature; (3) ‘normoxia’ (200-100 µM) versus hyperoxia (450-250 µM). The SUIT-008 protocol [6] was applied in all assays. Results were excluded from analysis if the cytochrome c flux control factor, FCFc = (IO2,cPM-IO2,PM)/IO2,cPM, exceeded 0.1 in the OXPHOS-state (Fig. 1; steps 2D and 2c). For abbreviations see Figure 1 and Gnaiger et al 2019 [7].
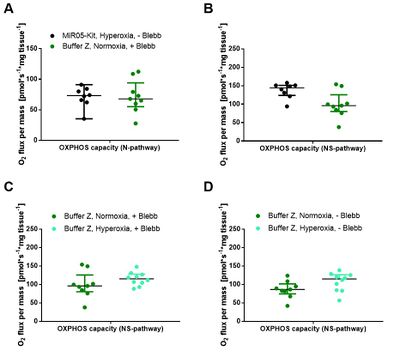
NS-OXPHOS capacity was oxygen-limited under ‘normoxic’ compared to hyperoxic conditions in both media (Figure 2A-D). Blebbistatin did not prevent the decrease of respiration in the ‘normoxic’ regime (Figure 2A and 2C), and exerted minor effects on oxygen flux in both media (Figure 2E-F). These results indicate that oxygen dependence is critical and independent of experimental buffers and blebbistatin (Figure 2A-D). Comparing respiratory capacity in both media under hyperoxic conditions, oxygen flux per mass was higher in MiR05-Kit than in Buffer Z (Figure 2E-F). Evaluation of these trends will be completed based on an in-depth statistical analysis. Our inter-laboratory study provides a basis to harmonize published results on permeabilized human skeletal muscle fibers and establishes guidelines for selecting optimum experimental conditions. - Extended abstract
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E & Beno M & Gnaiger C • O2k-Network Lab: AT Innsbruck Oroboros, AT Innsbruck Gnaiger E, US FL Orlando Goodpaster BH, DE Duesseldorf Roden M, DK Copenhagen Dela F, DK Copenhagen Larsen S, ES Barcelona Garcia-Roves PM
Affiliations
Doerrier C (1), Gama-Perez P (2), Distefano G (3), Pesta D (4),(5), Soendergaard SD (6), Chroeis KM (6), Gonzalez-Franquesa A (7), Goodpaster BH (3), Coen P (3), Larsen S (6), Gnaiger E (1),(8), Garcia-Roves PM (2)
- Oroboros Instruments, Innsbruck, Austria - [email protected]
- Dept Physiological Sciences, Univ Barcelona and Bellvitge Biomedical Research Inst, Spain
- Translational Research Inst Metabolism Diabetes, Florida Hospital, Orlando, FL, USA
- Inst Clinical Diabetology, German Diabetes Center, Leibniz Center Diabetes Research Heinrich-Heine Univ Düsseldorf
- German Center Diabetes Research, Munich, Neuherberg; Germany
- Dept Biomedical Sciences, Center Healthy Aging, Fac Health Sciences, Denmark
- The Novo Nordisk Center Basic Metabolic Research, Section Integrative Physiology; Univ Copenhagen, Denmark
- D Swarovski Research Lab, Dept Visceral, Transplant Thoracic Surgery, Med Univ Innsbruck, Austria
Support
- This preprint is based upon work from COST Action CA15203 MitoEAGLE, supported by COST (European Cooperation in Science and Technology).
Figures
References
- Scandurra FM, Gnaiger E (2010) Cell respiration under hypoxia: facts and artefacts in mitochondrial oxygen kinetics. Adv Exp Med Biol 662:7-25.
- Gnaiger E (2003) Oxygen conformance of cellular respiration. A perspective of mitochondrial physiology. Adv Exp Med Biol 543:39-55.
- Perry CG, Kane DA, Lin CT, Kozy R, Cathey BL, Lark DS, Kane CL, Brophy PM, Gavin TP, Anderson EJ, Neufer PD (2011) Inhibiting myosin-ATPase reveals a dynamic range of mitochondrial respiratory control in skeletal muscle. Biochem J 437:215-22.
- Bezuidenhout N, Doerrier C, Droescher S, Ojuka E, Gnaiger E (2016) Comparison of oxygen dependence of respiration in permeabilized mouse skeletal muscle fibers in two respiration media, MiR06Cr and Buffer Z containing Ctl, Cr and Blebbistatin. Abstract MitoFit Science Camp 2016.
- Baker M (2016) 1,500 scientists lift the lid on reproducibility. Survey sheds light on the ‘crisis’ rocking research. Nature 533:452–4.
- SUIT-008_O2_pfi_D014
- Gnaiger E, Aasander Frostner E, Abdul Karim N, Abumrad NA, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Adiele RC, et al (2019) Mitochondrial respiratory states and rates. MitoFit Preprint Arch doi:10.26124/mitofit:190001.v4.
Event
Preprints for Gentle Science
» MitoFit Preprints - the Open Access preprint server for mitochondrial physiology and bioenergetics
Labels: MiParea: Respiration, Instruments;methods
Organism: Human
Tissue;cell: Skeletal muscle
Preparation: Permeabilized tissue
Coupling state: LEAK, OXPHOS, ET
Pathway: N, S, NS, ROX
HRR: Oxygraph-2k
Preprints, MitoEAGLEPublication, Vastus lateralis, Blebbistatin







